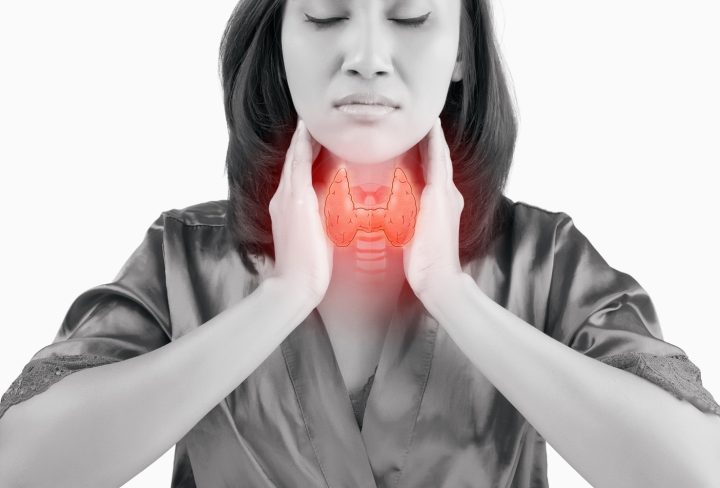
The thyroid is a tiny, butterfly-shaped gland which is in front of your windpipe. It produces and releases the hormones that help your body regulate and use energy.
Hypothyroidism means underactive thyroid; this occurs when your thyroid gland does not make sufficient thyroid hormones to meet your body’s demands.
Hypothyroidism Causes
Hypothyroidism is caused due to the following:
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: An autoimmune disorder where one’s own immune system attacks their own thyroid
- Iodine deficiency
- Thyroiditis (inflammation of the thyroid)
- Congenital (since birth) hypothyroidism
- Surgical removal of little or all the thyroid gland
- Radiation treatment of the thyroid
- Certain medicines
Hypothyroidism Risk Factors
You are at higher risk for hypothyroidism by:
- Being a woman
- >60 years
- Having a thyroid problem before, such as a goiter
- Previous thyroid surgery
- Radiation treatment for the thyroid gland, neck, or chest
- Family history of thyroid disease
- Pregnancy
- Turner syndrome (a female genetic disorder)
- Certain health conditions (rheumatoid arthritis, type 2 diabetes)
Hypothyroidism Symptoms
The symptoms of hypothyroidism may include:
- Fatigue
- Weight gain
- A puffy face
- Trouble tolerating cold
- Joint and muscle pain
- Constipation
- Dry skin
- Dry, thinning hair
- Decreased sweating
- Heavy or irregular menstrual periods
- Fertility problems in women
- Depression
- Slowed pulse rate
- Goiter, is an enlarged thyroid that makes the neck look swollen
Hypothyroidism Diagnosis
The diagnosis of hypothyroidism is made by performing the following diagnostic tests:
- A medical history, including asking about your signs and symptoms
- A physical examination
- Thyroid blood tests (To look for thyroid hormone levels (TSH, T3, T4) and thyroid antibody blood tests)
- Imaging tests like thyroid scans, ultrasound, or radioactive iodine uptake tests.
Hypothyroidism Treatment
The treatment is focused on replacing insufficient thyroid hormones with medications such as levothyroxine.
Hypothyroidism is an easily manageable disease. However, you must continuously take medication to normalize the amount of hormones in your body.
Hypothyroidism Complications
If hypothyroidism is undertreated, it could lead to below complications:
- Mental health problems
- Troublesome breathing
- Heart Problems
- Goiter (enlargement of the thyroid gland)
Hypothyroidism Diet
There are no specific diet recommendations for hypothyroidism patients but should follow a well-balanced diet that is low in fat or sodium.
Other foods and nutrients may be dangerous, especially if consumed in more quantities, which include:
- Soya, affects the thyroxine absorption
- Iodine
- Iron supplements, affects thyroxine absorption
- Cruciferous vegetables like cauliflower, kale, and cabbage may contribute to a goiter, but only if taken in large amounts
Any alterations to the diet or hypothyroidism supplements should be discussed with your doctor.
Conclusion
Hypothyroidism is a common condition that occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones leading to a variety of symptoms, including fatigue, weight gain, and depression. Hypothyroidism can be caused by a number of factors, including autoimmune disease, radiation therapy, and certain medications. Treatment for hypothyroidism often involves taking thyroid hormone replacement medication, which can help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. Additionally, making lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet and exercise routine can also be beneficial for managing hypothyroidism. Early diagnosis and treatment are important for preventing further complications and improving overall health and well-being.