Laparoscopy
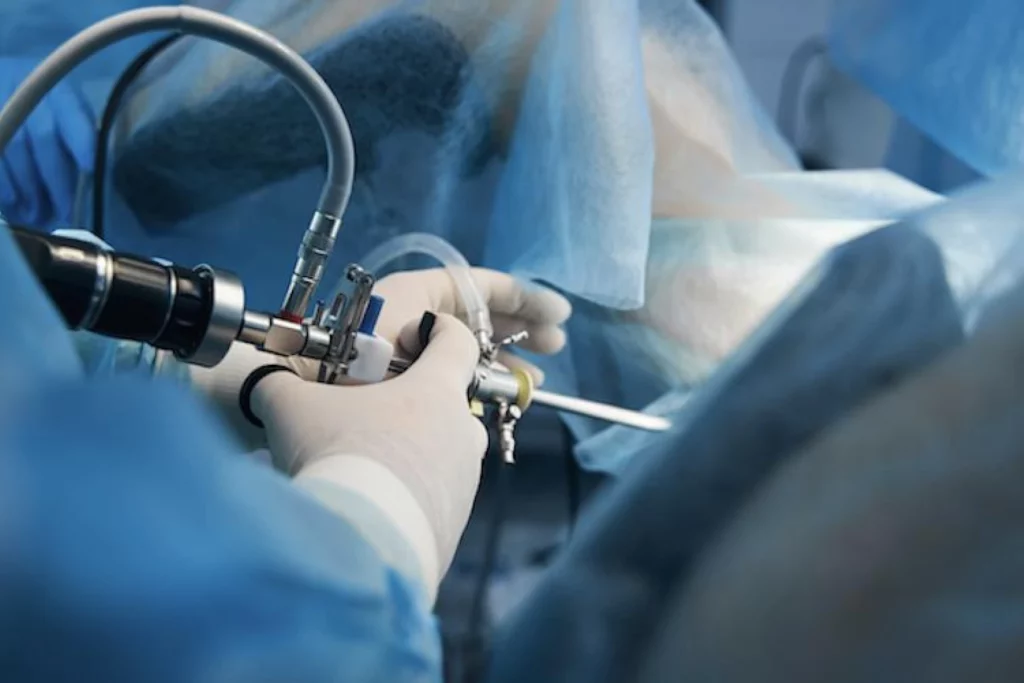
Laparoscopy, also known as minimally invasive surgery, is a surgical technique that uses small incisions and a camera to perform operations. It has revolutionized various fields of surgery, including gynecology, urology, and general surgery. The procedure involves inserting a laparoscope (a thin tube with a light and camera) through a small incision, often around the belly button, to allow surgeons to visualize internal organs on a monitor. Additional small incisions are made to introduce surgical instruments, enabling precise tissue manipulation.
Laparoscopy offers several advantages over traditional open surgery, including reduced pain, shorter recovery times, smaller scars, and less risk of infection. Common laparoscopic procedures include appendectomy, gallbladder removal, hernia repair, and gynecological surgeries like hysterectomy and endometriosis treatment.
One of the main benefits of laparoscopy is its ability to provide better visualization of the surgical area, enhancing precision. It also allows for quicker post-operative recovery, reducing the time spent in the hospital and enabling patients to return to daily activities sooner.
Despite its advantages, laparoscopy requires specialized skills, and not all procedures are suitable for this technique. Some patients may have conditions that make laparoscopy challenging or contraindicated. However, it remains a cornerstone of modern surgical practices due to its numerous benefits.


